Financial statements are an essential tool for any business or organization. They provide a snapshot of the company’s financial health and performance, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions. In this guide, we will delve into the world of financial statements, exploring their purpose, components, and how to interpret them.
DANH MỤC BÀI VIẾT
What are Financial Statements?

Definition and Purpose
Financial statements are formal reports that summarize a company’s financial performance over a specific period. They include information on revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. The primary purpose of financial statements is to provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of the company’s financial health and performance. These stakeholders may include investors, creditors, management, and regulatory bodies.
Importance of Financial Statements
Financial statements play a crucial role in the decision-making process for various stakeholders. Here are some reasons why they are essential:
- Investment Decisions: Investors rely on financial statements to determine whether to invest in a company or not. They use these reports to assess the company’s profitability, liquidity, and financial stability.
- Credit Decisions: Lenders and creditors use financial statements to evaluate a company’s creditworthiness before providing loans or extending credit.
- Business Operations: Management uses financial statements to analyze the company’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Compliance: Regulatory bodies require companies to submit financial statements for tax purposes and to ensure compliance with accounting standards.
Types of Financial Statements

There are four types of financial statements: income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in equity. Let’s explore each one in detail.
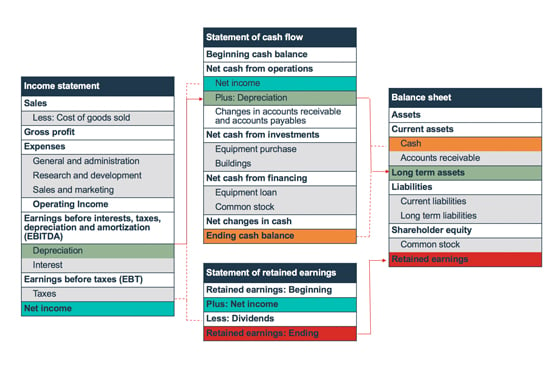
Income Statement
An income statement shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and net income or loss over a specific period. It provides an overview of how well the company has performed in terms of generating profits. The basic formula for an income statement is:
Net Income = Revenue – Expenses
The income statement is divided into three sections: operating, non-operating, and income tax.
- Operating: This section includes revenues and expenses directly related to the company’s core business activities.
- Non-operating: Non-operating items include revenues and expenses that are not directly related to the company’s main operations, such as interest income or expenses.
- Income Tax: This section shows the company’s tax liability based on its taxable income.
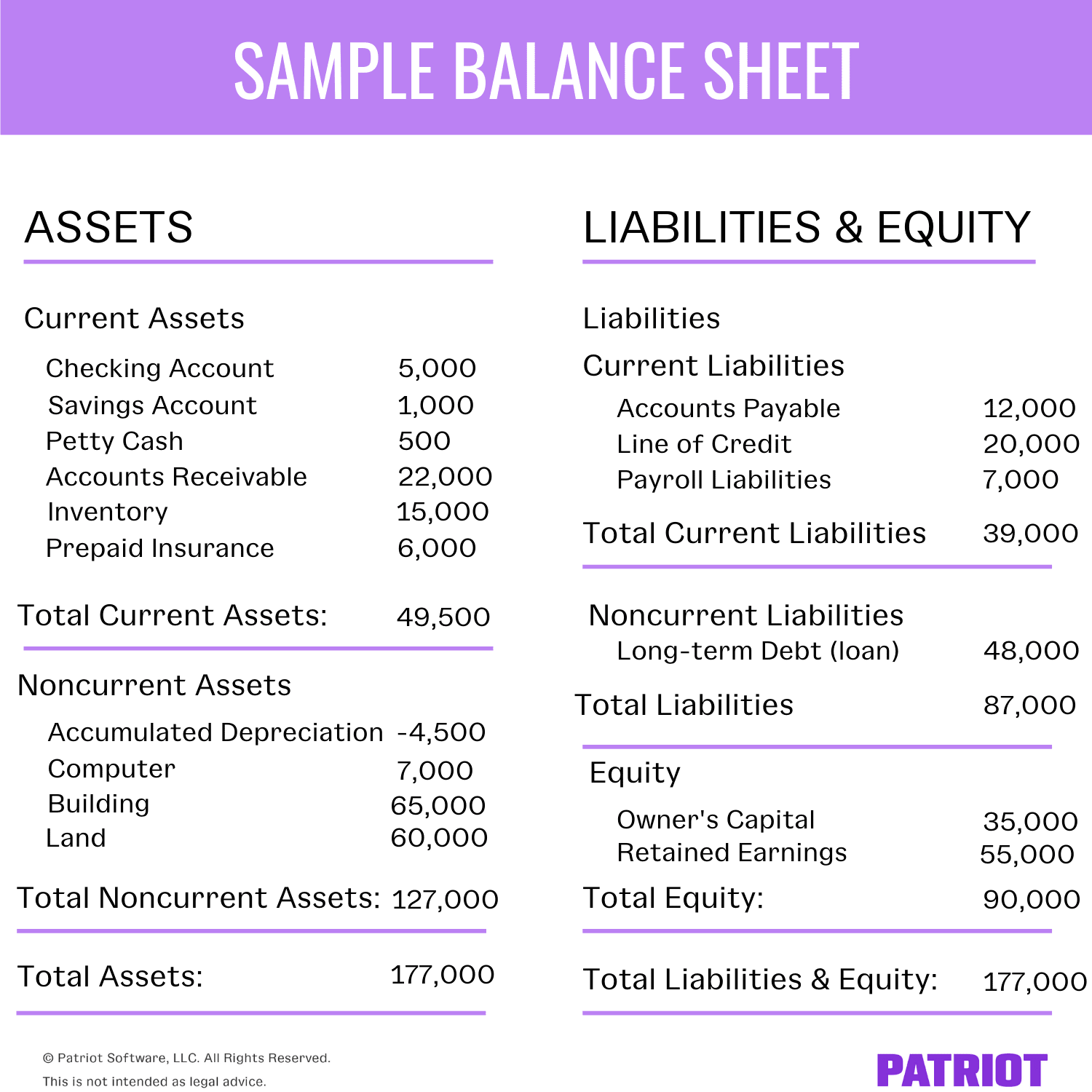
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It lists the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, following the fundamental accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
The balance sheet is divided into two sides: the left side shows assets, while the right side shows liabilities and equity. Assets are further categorized as current or non-current, while liabilities are classified as current or long-term.
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement shows how much cash is coming in and going out of a company during a specific period. It is divided into three sections: operating, investing, and financing activities.
- Operating Activities: This section shows the cash inflow and outflow from the company’s core business operations.
- Investing Activities: Investing activities include cash flows from buying or selling long-term assets, such as property, plant, and equipment.
- Financing Activities: This section includes cash flows from obtaining or repaying loans, issuing or buying back stock, and paying dividends.
Statement of Changes in Equity
The statement of changes in equity shows how the company’s equity has changed over a specific period. It includes information on the company’s common stock, retained earnings, and other comprehensive income.
Interpreting Financial Statements
Interpreting financial statements can seem like a daunting task, but with a basic understanding of their components, it becomes more manageable. Here are some tips for analyzing financial statements:
- Compare to Previous Periods: Comparing current financial statements to previous periods can help identify trends and changes in the company’s financial performance.
- Use Ratios: Financial ratios can provide valuable insights into a company’s overall financial health. Some common ratios include profitability, liquidity, and solvency ratios.
- Read Footnotes: Footnotes provide additional information and explanations for the numbers presented in the financial statements. They can help clarify any uncertainties or discrepancies.
- Consider Industry Standards: It’s essential to take into account the industry in which the company operates when analyzing financial statements. Different industries may have different financial benchmarks and standards.
Common Questions about Financial Statements

What is the difference between a balance sheet and an income statement?
Both balance sheets and income statements provide important information on a company’s financial performance, but they differ in terms of what they show. A balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, while an income statement shows the company’s performance over a specific period.
Can financial statements be manipulated?
Unfortunately, financial statements can be manipulated or misrepresented. This is why it’s crucial to analyze them thoroughly, compare them to previous periods, and consider industry standards.
How often should financial statements be prepared?
Financial statements are usually prepared on a quarterly and annual basis. However, some companies may choose to prepare them on a monthly basis for more frequent analysis.
Are there any limitations to financial statements?
Yes, there are limitations to financial statements. They only provide a snapshot of the company’s financial performance at a specific point in time and may not accurately reflect the company’s future performance.
What should I do if I don’t understand the financial statements?
If you are having trouble understanding financial statements, it’s best to seek advice from a financial professional. They can help interpret the numbers and provide a better understanding of the company’s financial performance.
Conclusion
Financial statements are an essential tool for understanding a company’s financial health and performance. They provide valuable information to stakeholders and help guide decision-making. By understanding the different types of financial statements and how to interpret them, you can gain valuable insights into the company’s financial standing. Always remember to consider industry standards and compare to previous periods when analyzing financial statements.